Product Description
Feature
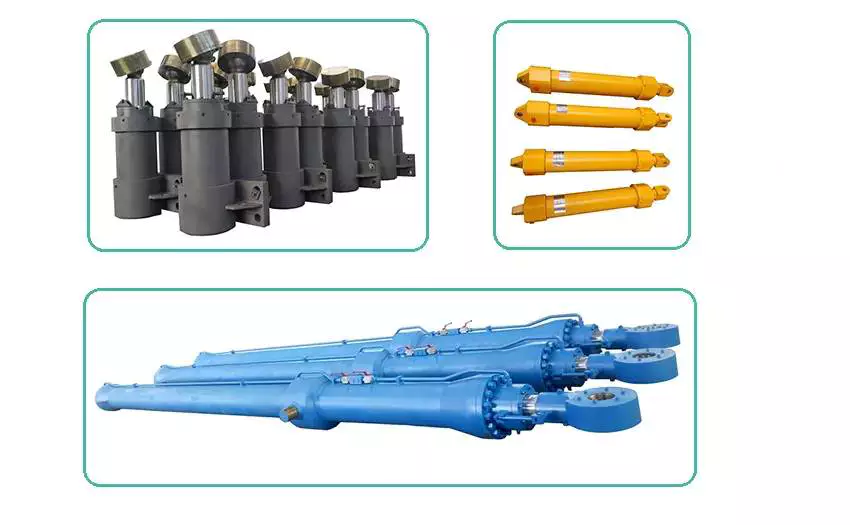
1)Designed and manufactured according to JIS-B8367 standard
2)Four-rod design, versatility, ease of maintenance.
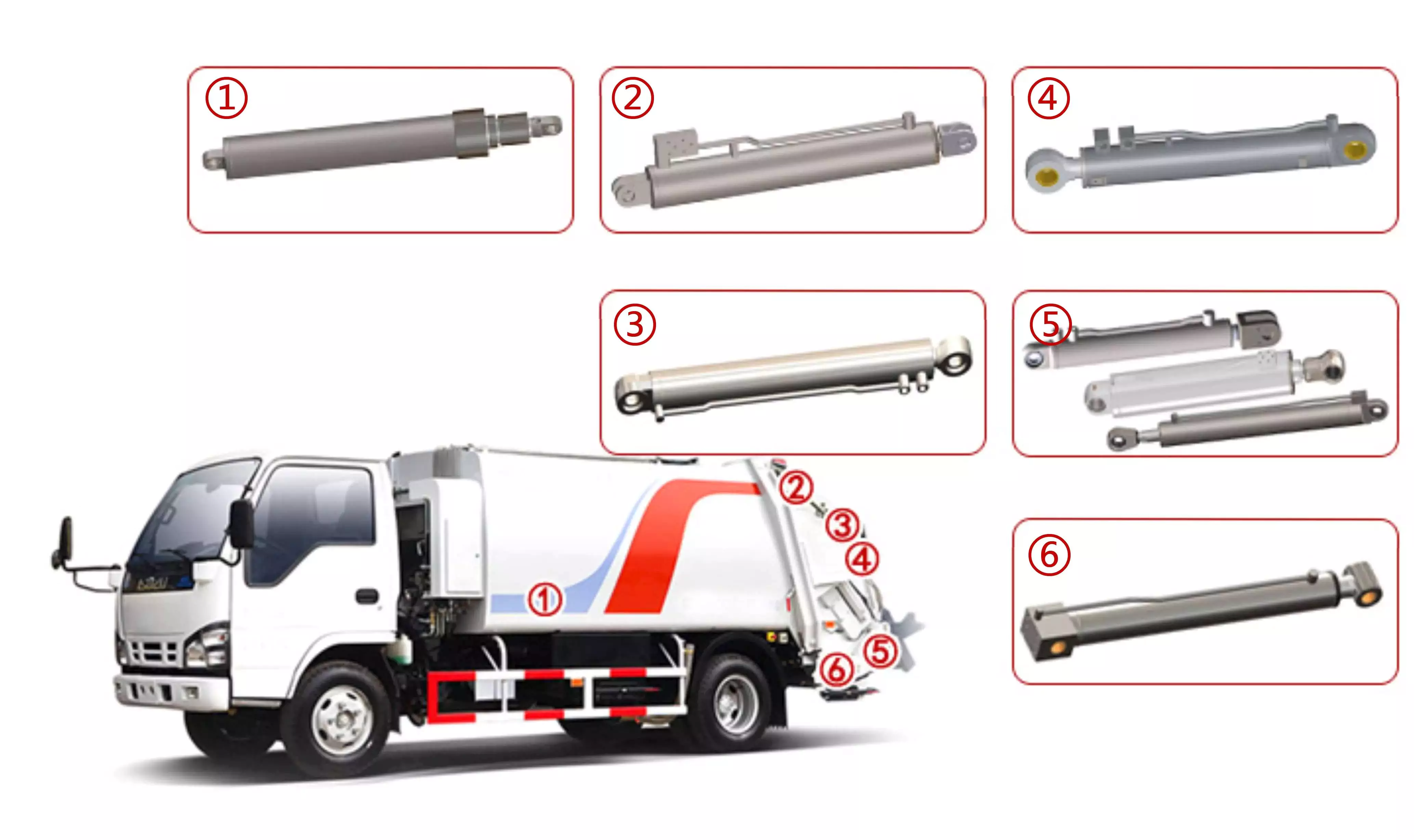
3) Variety of installation types for customers to choose.
4) All seals adopt foreign famous brand specifications.
Oil seal material
Order form
External dimensions
About us
Jufan Technology Inc., was established in June 1979, has been in automation industry for more than 25 years and now is 1 of major makers to produce pneumatic, hydraulic, and vacuum related products and to serve as system integrator of fluid power and transmission control fields
After years of product development and quality improvement, CHINAMFG has been able to produce and to sell products to industrialized countries such as Japan, America, and European Union by utilizing the capacity of 2 major facilities. One is located in ZheJiang and the other is at HangZhou China.
Packaging & Delivery
FAQ
Q1: Is CHINAMFG a manufacturer or a trading company?
We have our own factory, so we can provide the best price as well the first service.
Q2: Do you accept customization or Non-standard products?
Yes, we can customize products as the customers required.
Q3: What is your MOQ?
MOQ depends on our clients needs. Besides, we welcome trial order before mass production.
Q4: How long is your delivery time?
Normally, the delivery time is 7 days if we have stock. If we don’t have stock, it needs 15-30 working days. And it also depends on the quantity and requirements of products.
Q5: What are your payment terms?
T/T. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | Medium Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | Normal Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Double Acting |
| Working Method: | Straight Trip |
| Adjusted Form: | Regulated Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do hydraulic cylinders compare to other methods of force generation like electric motors?
Hydraulic cylinders and electric motors are two different methods of force generation with distinct characteristics and applications. While both hydraulic cylinders and electric motors can generate force, they differ in terms of their working principles, performance attributes, and suitability for specific applications. Here’s a detailed comparison of hydraulic cylinders and electric motors:
1. Working Principle:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders generate force through the conversion of fluid pressure into linear motion. They consist of a cylinder barrel, piston, piston rod, and hydraulic fluid. When pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, causing the piston rod to extend or retract, thereby generating linear force.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors generate force through the conversion of electrical energy into rotational motion. They consist of a stator, rotor, and electromagnetic field. When an electrical current is applied to the motor’s windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor, causing it to rotate and generate torque.
2. Force and Power:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are known for their high force capabilities. They can generate substantial linear forces, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that require lifting, pushing, or pulling large loads. Hydraulic systems can provide high force output even at low speeds, allowing for precise control over force application. However, hydraulic systems typically operate at lower speeds compared to electric motors.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors excel in providing high rotational speeds and are commonly used for applications that require rapid motion. While electric motors can generate significant torque, they tend to have lower force output compared to hydraulic cylinders. Electric motors are suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.
3. Control and Precision:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems offer excellent control over force, speed, and positioning. By regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and speed of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely controlled. Hydraulic systems can provide gradual acceleration and deceleration, allowing for smooth and precise movements. This level of control makes hydraulic cylinders well-suited for applications that require precise positioning, such as in industrial automation or construction equipment.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors also offer precise control over speed and positioning. Through motor control techniques such as varying voltage, frequency, or pulse width modulation (PWM), the rotational speed and position of electric motors can be accurately controlled. Electric motors are commonly used in applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics, CNC machines, or servo systems.
4. Efficiency and Energy Consumption:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems can be highly efficient, especially when properly sized and designed. However, hydraulic systems typically have higher energy losses due to factors such as fluid leakage, friction, and heat generation. The overall efficiency of a hydraulic system depends on the design, component selection, and maintenance practices. Hydraulic systems require a hydraulic power unit to pressurize the hydraulic fluid, which consumes additional energy.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors can have high efficiency, especially when operated at their optimal operating conditions. Electric motors have lower energy losses compared to hydraulic systems, primarily due to the absence of fluid leakage and lower friction losses. The overall efficiency of an electric motor depends on factors such as motor design, load conditions, and control techniques. Electric motors require an electrical power source, and their energy consumption depends on the motor’s power rating and the duration of operation.
5. Environmental Considerations:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems typically use hydraulic fluids that can pose environmental concerns if they leak or are not properly disposed of. The choice of hydraulic fluid can impact factors such as biodegradability, toxicity, and potential environmental hazards. Proper maintenance and leak prevention practices are essential to minimize the environmental impact of hydraulic systems.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors are generally considered more environmentally friendly since they do not require hydraulic fluids. However, the environmental impact of electric motors depends on the source of electricity used to power them. When powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, electric motors can offer a greener solution compared to hydraulic systems.
6. Application Suitability:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used in applications that require high force output, precise control, and durability. They are widely employed in industries such as construction, manufacturing, mining, and aerospace. Hydraulic systems are well-suited for heavy-duty applications, such as lifting heavy objects, operating heavy machinery, or controlling large-scale movements.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors are widely used in various industries and applications that require rotational motion, speed control, and precise positioning. They are commonly found in appliances, transportation, robotics, HVAC systems, and automation. Electric motorsare suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.In summary, hydraulic cylinders and electric motors have different working principles, force capabilities, control characteristics, efficiency levels, and application suitability. Hydraulic cylinders excel in providing high force output, precise control, and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Electric motors, on the other hand, offer high rotational speeds, precise speed control, and are commonly used for applications that involve continuous rotary motion. The choice between hydraulic cylinders and electric motors depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of motion, force output, control precision, and environmental considerations.
Integration of Hydraulic Cylinders with Equipment Requiring Rapid and Dynamic Movements
Hydraulic cylinders can indeed be integrated with equipment that requires rapid and dynamic movements. While hydraulic systems are generally known for their ability to provide high force and precise control, they can also be designed and optimized for applications that demand fast and dynamic motion. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders can be integrated with such equipment:
- High-Speed Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic cylinders can be part of high-speed hydraulic systems designed specifically for rapid and dynamic movements. These systems incorporate features such as high-flow valves, optimized hydraulic circuitry, and responsive control systems. By carefully engineering the system components and hydraulic parameters, it is possible to achieve the desired speed and responsiveness, enabling the equipment to perform rapid movements.
- Valve Control: The control of hydraulic cylinders plays a crucial role in achieving rapid and dynamic movements. Proportional or servo valves can be used to precisely control the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the cylinder. These valves offer fast response times and precise flow control, allowing for rapid acceleration and deceleration of the cylinder’s piston. By adjusting the valve settings and optimizing the control algorithms, equipment can be designed to execute dynamic movements with high speed and accuracy.
- Optimized Cylinder Design: The design of hydraulic cylinders can be optimized to facilitate rapid and dynamic movements. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys or composite materials, can be used to reduce the moving mass of the cylinder, enabling faster acceleration and deceleration. Additionally, the cylinder’s internal components, such as the piston and seals, can be designed for low friction to minimize energy losses and enhance responsiveness. These design optimizations contribute to the overall speed and dynamic performance of the equipment.
- Accumulator Integration: Hydraulic accumulators can be integrated into the system to enhance the dynamic capabilities of hydraulic cylinders. Accumulators store pressurized hydraulic fluid, which can be rapidly released to supplement the flow from the pump during high-demand situations. This stored energy can provide an extra boost of power, allowing for faster and more dynamic movements. By strategically sizing and configuring the accumulator, the system can be optimized for the specific rapid and dynamic requirements of the equipment.
- System Feedback and Control: To achieve precise and dynamic movements, hydraulic systems can incorporate feedback sensors and advanced control algorithms. Position sensors, such as linear potentiometers or magnetostrictive sensors, provide real-time position feedback of the hydraulic cylinder. This information can be used in closed-loop control systems to maintain precise positioning and execute rapid movements. Advanced control algorithms can optimize the control signals sent to the valves, ensuring smooth and dynamic motion while minimizing overshooting or oscillations.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders can be integrated with equipment that requires rapid and dynamic movements by utilizing high-speed hydraulic systems, employing responsive valve control, optimizing cylinder design, integrating accumulators, and incorporating feedback sensors and advanced control algorithms. These measures enable hydraulic systems to deliver the speed, responsiveness, and precision necessary for equipment operating in dynamic environments. By leveraging the capabilities of hydraulic cylinders, manufacturers can design and integrate systems that meet the requirements of applications demanding rapid and dynamic movements.

How do hydraulic cylinders accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements?
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements, providing flexibility and adaptability for different applications. They can be tailored to meet specific needs by considering factors such as piston diameter, rod diameter, hydraulic pressure, and cylinder design. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements:
1. Cylinder Size and Design:
– Hydraulic cylinders come in various sizes and designs to accommodate different stroke lengths and force requirements. The cylinder’s diameter, piston area, and rod diameter are key factors that determine the force output. Larger cylinder diameters and piston areas can generate greater force, while smaller diameters are suitable for applications requiring lower force. By selecting the appropriate cylinder size and design, stroke lengths and force requirements can be effectively accommodated.
2. Piston and Rod Configurations:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be designed with different piston and rod configurations to accommodate variations in stroke length. Single-acting cylinders have a single piston and can provide a stroke in one direction. Double-acting cylinders have a piston on both sides, allowing for strokes in both directions. Telescopic cylinders consist of multiple stages that can extend and retract, providing a longer stroke length compared to standard cylinders. By selecting the appropriate piston and rod configuration, the desired stroke length can be achieved.
3. Hydraulic Pressure and Flow:
– The hydraulic pressure and flow rate supplied to the cylinder play a crucial role in accommodating variations in force requirements. Increasing the hydraulic pressure increases the force output of the cylinder, enabling it to handle higher force requirements. By adjusting the pressure and flow rate through hydraulic valves and pumps, the force output can be controlled and matched to the specific requirements of the application.
4. Customization and Tailoring:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be customized and tailored to meet specific stroke length and force requirements. Manufacturers offer a wide range of cylinder sizes, stroke lengths, and force capacities to choose from. Additionally, custom-designed cylinders can be manufactured to suit unique applications with specific stroke length and force demands. By working closely with hydraulic cylinder manufacturers, it is possible to obtain cylinders that precisely match the required stroke length and force requirements.
5. Multiple Cylinders and Synchronization:
– In applications that require high force or longer stroke lengths, multiple hydraulic cylinders can be used in combination. By synchronizing the movement of multiple cylinders through the hydraulic system, the stroke length and force output can be effectively increased. Synchronization can be achieved using mechanical linkages, electronic controls, or hydraulic circuitry, ensuring coordinated movement and force distribution across the cylinders.
6. Load-Sensing and Pressure Control:
– Hydraulic systems can incorporate load-sensing and pressure control mechanisms to accommodate variations in force requirements. Load-sensing systems monitor the load demand and adjust the hydraulic pressure accordingly, ensuring that the cylinder delivers the required force without exerting excessive force. Pressure control valves regulate the pressure within the hydraulic system, allowing for precise control and adjustment of the force output based on the application’s needs.
7. Safety Considerations:
– When accommodating variations in stroke length and force requirements, it is essential to consider safety factors. Hydraulic cylinders should be selected and designed with an appropriate safety margin to handle unexpected loads or variations in operating conditions. Safety mechanisms such as overload protection valves and pressure relief valves can be incorporated to prevent damage or failure in situations where the force limits are exceeded.
By considering factors such as cylinder size and design, piston and rod configurations, hydraulic pressure and flow, customization options, synchronization, load-sensing, pressure control, and safety considerations, hydraulic cylinders can effectively accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements. This flexibility allows hydraulic cylinders to be tailored to meet the specific demands of a wide range of applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.

editor by CX 2023-10-15